If you are an avid golfer, you probably have played on a golf simulator before; if not at home, then maybe at your favorite golf shop or club. The process seems very simple: just stand in the teeing area, swing your club, and hit the golf ball. Everything is immediately calculated, and your shot is simulated and displayed on the hitting screen (along with measurements and readings).
However, many hardware and software components come into play in virtual golf: a computer, projector, simulation software, and launch monitor. Each component does specific tasks to contribute to the final simulation.
In this article, we will be exploring the ins and outs of the top golf simulator packages.
In the end, you will have a detailed answer to the question: How does a golf simulator work?
- 1) What Is a Golf Simulator?
- 2) Composition of a Typical Golf Simulator System
- 3) Types of Golf Simulators Tracking Technologies
- 4) How Does a Golf Simulator Work? (Process Breakdown)
- 5) Parameters Measured by Golf Simulators
- 6) How Does Putting Work on a Golf Simulator?
- 7) Will a Golf Simulator Help Your Game?
- 8) Final Thoughts
What Is a Golf Simulator?
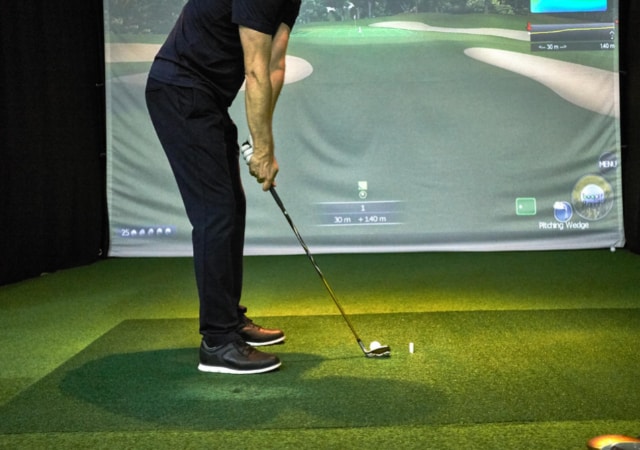

A golf simulator system is a combination of several components that work together to provide a virtual golf experience that is more or less realistic and accurate based on many different factors, such as the price and technologies used to produce the components.
The two main parts of a golf simulator are the graphics display unit, which displays the virtual image of the course being played, and the motion sensor, which detects the position and orientation of the player relative to the screen. The computer calculates the location of objects in relation to the player’s viewpoint and projects them onto the screen using a variety of methods including ray tracing, rasterization, and vector drawing.
The detection part usually takes place in the golf launch monitor, using different types of sensors. After that, the detected data is sent to the simulation software (usually installed on a computer). Next, the computer does different calculations and sends the outcome (picture) to the projector that finally displays everything on the impact screen.
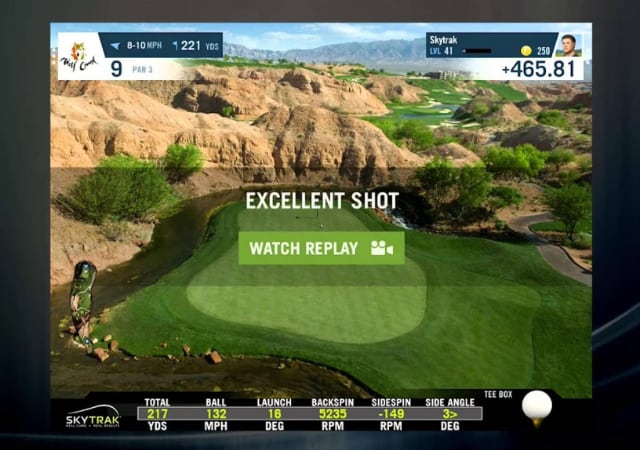
In addition to simulating your shots on a virtual course or driving range, golf simulators provide numerous data about your golf shot, club, and ball. These include ball speed, launch angle, club speed, club path, spin rate, ball path, horizontal and vertical launch angle, flight path, carry distance, etc.
The quality and accuracy of all of these components is the main determining factor that affects the simulation outcome and the price of the package (Better packages use better technology and components and cost more money).
Composition of a Typical Golf Simulator System
When buying a new golf simulator system, golfers can go for two different options. First, they can pick individual components to buy and build their own simulator. To do this, golfers need to have some knowledge to avoid buying incompatible components.
The second option is to buy a complete golf simulator system that includes everything you will need to use the package. Just install everything and make sure everything is correctly plugged in to start playing without too much hassle. That’s what most golfers do when buying a new system.
A complete package means less time spent looking for components and less risk of ending up with incompatible components (not working together). In addition, the software components are usually pre-installed and the components are guaranteed to work without issues.
Sometimes, the manufacturer offers the free setup for their purchased packages: A team of technicians arrives with the package to take care of its installation in the designated room.
The installation team also helps the customer get used to the simulation features, interface, and settings (like the HD Golf simulator package, for instance).
Let’s now focus on the contents of a typical golf simulator package:
Projection System
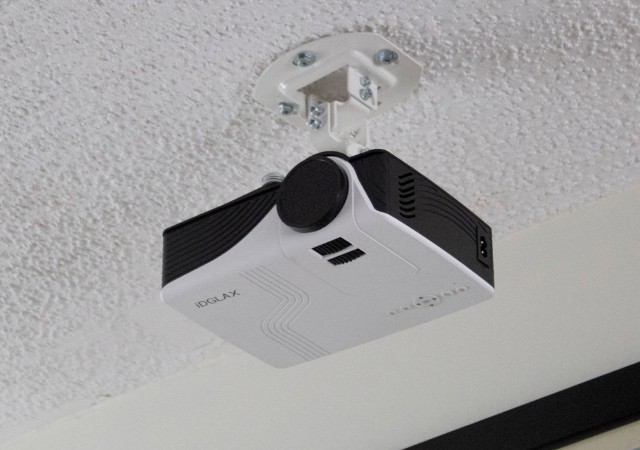

Golf simulator packages, such as SkyTrak, use and include a projector to display the simulation on the golf simulator screen. The pricier packages come with higher-quality projectors to provide the best possible graphics quality. Also, the more expensive models are capable of projecting in ultra-high quality with resolutions of up to 1080P (1920 x 1080 pixels), 4k (3840 x 2160 pixels), and even 8K (7680 × 4320 pixels). The higher the resolution, the better the image quality and simulation experience (and the more powerful the required computer configuration is).
There are different types of projectors that are manufactured today. Each type is useful in certain specific setups. For example, golf simulator manufacturers usually include short-throw projectors with their packages.
This type of projector is usually mounted at a distance of between three to eight feet away from the screen. The benefit of using a short-throw projector is that it helps eliminate eye glare and shadows.
The best projectors are manufactured by popular brands, including Optoma, Sony, BenQ, Panasonic, Epson, etc. Make sure your simulator includes a good-quality projector, as the whole virtual experience depends on it!
Creating a realistic and immersive golf simulation experience requires careful consideration beyond just the projector and screen. Lighting plays a crucial role in mimicking the look and feel of being on a real course. Factors like ambient light level, light direction, and color temperature can significantly impact your perception and performance.
Audio System

Golf simulator packages also come with an included audio system that can be used to simulate different sounds in the virtual golf course or to command the detection sensors to start measuring data that will be used for the simulation and displayed on the screen (As some packages offer voice command, which triggers optical sensors).
Most commonly, golf simulators opt for quality stereo sound systems to provide audio for the simulation and make it more realistic. On the other hand, high-end golf simulation packages from companies like HD Golf, Foresight Sports, Golfzon, and others offer surround sound configurations to make the whole experience even more immersive and realistic. At the very least, these companies will offer the option to include a surround sound system from a company like Sony, Sennheiser, Yamaha, Dali, Sonos, etc. These can be purchased separately and used with the simulation system. They are also very useful for those who want to use their packages as entertainment centers or home theaters when they are not playing golf on them.
You can expect a good surround system to cost a lot of money; for example, the best systems can cost (at least) upwards of 1,000 dollars (adding to the initial cost of the package). Still, consider it an investment, as it takes the sound quality and overall experience to a whole new level.
Ball Flight Tracker & Swing Analysis
This is where most golfers consider virtual golf to be superior to playing on a real golf course. When using an indoor golf simulator, you can get many readings and data concerning your swing, golf ball, and club movement. You can get instant feedback on your swings so that you know what you are doing right or wrong. This can significantly help you track your progress and improve your overall game.
The detection, tracking, and analysis processes are carried out in the golf launch monitor. It is a very important component of your package, as it is the one that includes sensors (of different types- more on that later) that will track your swing metrics and provide instant feedback that is then used by the computer (and simulation software) to simulate your shot and display it on the screen.
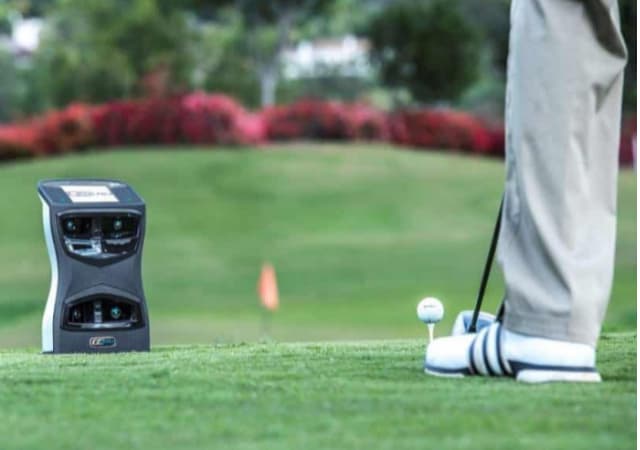

Almost all big manufacturers of golf simulators produce their own, in-house launch monitors using different technologies to detect all the details of your swings and provide data used as the base for the whole simulation process. Also, launch monitors can cost anywhere between a few hundred dollars to up to thousands of dollars, depending on the technology they use and the number of readings and feedback they provide.
Pricier models of launch monitors provide much more data than cheaper models. However, all launch monitors will minimally offer data about things like clubface angle, carry distance, total distance, swing path, tempo, clubhead speed, etc.
Premium-quality golf simulators give you more data and feedback about your club and ball to help you improve your swing. Some manufacturers include exclusive technologies to provide data that no other manufacturer does; this is the case with HD Golf: Their Ultimate series golf simulators integrate pressure-sensitive hitting mats that use around 600 individual sensors to detect your balance and weight shift.
Virtual Golf Course (Simulation Software)
A golf simulator package comes with a simulation software (or bundle of software) that does the simulation process based on data captured through the launch monitor.
Typically, simulation software includes a number of virtual golf courses and driving ranges. They can also include challenges and mini-games to help you practice and improve your game. Usually, manufacturers provide access to a limited number of courses in their software, with the possibility to buy new ones (or packs of courses) to add to your library. Once again, more expensive packages will offer more courses out of the box in better visual quality.
The simulation software may also provide the possibility to record videos of your shots for future reference and comparison. Sometimes, the purchased software gives you access to platforms intended to teach golfers how to get better and to upload their collected data for analysis. In the end, you can get summaries of your performance and improvement.
Multiplayer is another feature offered by a lot of simulation software. You can play alone or against your friends or family members. It is also possible to play online rounds against other players from all around the world.
The features you get in your software package depend on what specific software is included. Premium-quality simulators usually come with in-house developed software bundles; other manufacturers choose to include support for various software solutions to choose from while buying your package.
Some of the best simulator software supported over multiple platforms include The Golf Course (TGC), E6 Connect, FSX (by Foresight Sports), Uneekor’s Refine, etc.
What Does a Complete Golf Simulator Package Include?
Different brands of golf simulators offer different degrees of accuracy, realism, visual quality, etc. The virtual golf experience is different between an entry-level package (like the OptiShot 2) and a premium one (like HD Golf or Trackman). The included components affect the final price of the unit. The more expensive the components are, the pricier the package will be and the more features and data it will provide. That just makes sense.
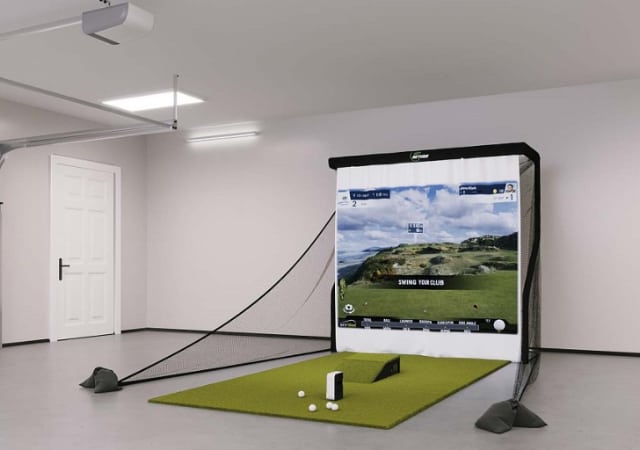

Basically, all golf simulators need to have the same components, regardless of their prices or the quality of the included components. Therefore, all packages must have the following:
- A software component to do the actual simulation.
- A detection device with sensors to detect ball and club movement and provide data used and displayed by the software. This device is usually a launch monitor connected to sensors (IR sensors, radar, or high-speed cameras).
- A computer to run the software and process the data to simulate the shots graphically. Having a decent configuration on your computer can help drastically with the visual quality of the simulation, as the computer will be able to process the graphics at the highest possible settings. It will also help you avoid any graphical glitches, lags or stutters.
- A projector or any display device to show the simulation. Even though it will be possible to hook your computer to your big-screen TV (and save some money), this is not recommended, as missed shots can result in rogue balls that may destroy your TV. That’s why golfers usually opt for a projector to display the simulation on a hitting screen.
- A golf simulator enclosure that contains all the elements needed to play your round of virtual golf. The enclosure contains the screen, hitting net, side barriers and netting, a hitting mat, and some turf. High-end simulator packages do come with complete enclosures specifically designed for them. Still, there are other enclosures that are used with many different packages. A good example is Shop Indoor Golf‘s SIG 8, SIG 10, and SIG 12 enclosures. They are excellent enclosures that contain everything needed to play virtual golf at home. The experience is even better if you go for the SIG golf simulator flooring (optional) that provides a very large playing area.
- Moreover, some packages include ceiling mounts for the projector or special mounting systems for the launch monitor and the sensors it uses (like high-speed cameras).
Types of Golf Simulators Tracking Technologies
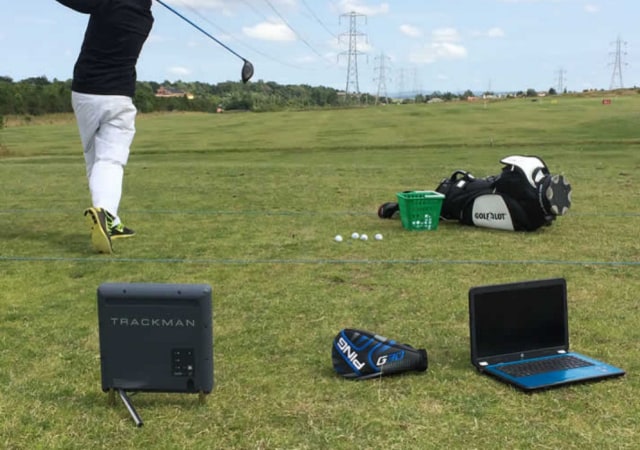

Nowadays, simulators use different technologies to track and detect movements and provide feedback and data. Different types of sensors are used to give readings of the player’s game. The three main types of used technologies are as follows:
Photometric
Photometric technology refers to Laser Light Detection And Ranging (L.I.D.A.R.). These methods work together to create a 3D model of the environment surrounding the player. This information is displayed on the screen for the user to see. In addition, this type of simulation provides accurate tracking of the clubhead movement during each shot.
This method uses light beams projected onto objects in order to determine the distance between two points. These lights reflect off the object back towards the sensor, where they are detected and analyzed. This technology provides a high level of accuracy. An example of the most well-known launch monitors using the photometric system is Skytrak.
Similar to a photometric system is the triscopic system, an example of which is the Foresight Sports GC3. It takes three high-speed images of the ball from three different angles, which increases the accuracy of the measurements.
You can go even further with the quadrascopic systems, which use four cameras to produce highly accurate measurements. The most well-known launch monitor using this system is the GCQUAD.
Radar (Doppler)
A Doppler radar uses a laser beam detection system that measures velocity based on Doppler shift/effect. This technique works by sending out pulses of microwave radiation toward the target. When these waves strike the moving object, they bounce back slightly faster because of its motion. This type of radar technology is very efficient at determining an object’s speed. It provides very accurate results. It is the same technology used by police to track speeders.
By measuring how fast the reflected wave returns, we know how far away the object is. With this knowledge, we can calculate the object’s velocity.
Examples of launch monitors using doppler radar technology: Flightscope Mevo and Mevo+, Voice Caddie Sc300i, and Ernest Sports ESB1.
Infrared (I.R.)
Infrared technology uses infrared rays to measure distances from one point to another. Infrared rays have wavelengths longer than visible light, making them invisible to our eyes. They travel through the air, water, and other materials without being absorbed.
I.R. systems consist of a transmitter and receiver connected with cables. A cable connects the transmitter to the camera lens while another connects the receiver to the monitor.
As the device moves closer to the object, more energy reaches the detector. I.R. cameras also have built-in algorithms that make calculations about the position of the object.
In general, I.R. systems are less expensive than photometric ones. However, they cannot accurately measure distances over long ranges.
For example, if you want to simulate driving 100 yards down the fairway, you will not get good results using an I.R. system.
The most well-known example using the infrared system is the Optishot 2.
How Does a Golf Simulator Work? (Process Breakdown)

Golf simulators operate just like computers. First, you stand on a swing pad, facing the screen; when you swing your club, the simulator gets input from detection hardware such as light sensors (cameras), radars, or infrared sensors. These sensors capture the details of the shot like club and ball speed, spin rates, smash factor, etc. The collected data is then processed by the computer (or tablet), simulated, and finally sent as output for the projector to display on the screen.
1. Taking Input
Input is everything detected by the detection hardware. Depending on the simulation package, the detection hardware (or input devices) can be high-speed cameras (in the case of a photometric simulator), radar Doppler sensors, or Infrared sensors.
The detection hardware detects various metrics related to your shot (input about your golf swing, club head, and ball). The amount of data you get depends on the simulator you have and the technology it uses. The input is then sent to the golf simulation software to be processed.
2. Processing of Data and Analysis
The golf simulation software is executed on dedicated hardware, such as a computer or tablet (Usually computers are favored as they offer higher performance). Choosing the right computer option can make the entire virtual experience or break it. The collected data is processed, analyzed by the software, and then simulated into virtual graphics that mimic what your swing (and overall shot) would be like on an actual golf course.
Depending on your golf simulator, the collected data, in the form of simple numbers related to your swing metrics or even videos that are meant to provide feedback on your shot are also processed. The data of all your virtual golf sessions may be compiled and organized in charts for future comparison and reference.
3. Delivering Output
After the input is collected and processed into 3D graphics by the input devices and processing hardware, respectively, the player needs output that simulates his/her shot.
The output is managed by the projector that displays the simulation as well as any feedback on the display screen. Camera-based systems can even provide feedback in the form of video playback of your shots with useful metrics overlay. Simulators like HD Golf offer the possibility of drawing or writing over the recorded video for you to mark any important details of the shot.
Many simulator software manufacturers offer online platforms for the players to save and compare their data and track their performance over a specific period of time.
Parameters Measured by Golf Simulators
If you have played virtual golf before, then you may have come across some terminology that is a bit difficult to understand, most of which is related to the data measured and provided by the simulator. Not understanding that terminology may affect the efficiency of the virtual golf sessions, as they are necessary to monitor your progress.
Let’s now go through some of the most common data and terminology used by almost all golf simulators:
Club Speed
Clubhead speed refers to the velocity of the clubhead during the swing. Club (head) speed is very important in both actual and virtual golf. It affects your total flight distance, as it is possible for each additional 1 MPH in clubhead speed to increase distance by around 3 yards when using the driver.
Ball Speed
The speed of the ball is measured immediately after impact with the clubhead. This metric is highly affected by clubhead speed and impact. In other words, a higher club speed combined with the correct impact angle will most likely produce a higher ball speed and travel distance.
The highest golf ball speed to ever be measured was in the 2014 World Long Drive Championship where Conor Powers achieved a ball speed of 226 MPH.
Launch Angle
Launch angle refers to the angle at which the ball leaves the tee or mat after impact. It is expressed in degrees. For instance, a launch angle of 20 degrees means that the ball ascends at a 20-degree angle from the surface it was struck from. So, the launch angle expresses how high or low the ball will fly after impact.
The term is associated by most golfers with drivers, and many factors contribute to the ball’s launch angle. For example, the clubface loft is the biggest factor that affects the ball’s launch angle, as will clubhead speed, angle of attack (how the clubhead approaches the ball), and the position of the clubhead at impact. The combination of all three factors determines the ball’s launch angle (and the same club can produce different launch angles in the hands of different golfers).
Face Angle
Face angle is the way the clubface is pointed at impact relative to the target line. The clubface can be pointed towards the right or the left.
Many golfers would refer to this as having a “square”, “open” or “closed” clubface. A square face means that the clubface is aligned with and facing the target line. With an open face, it is slightly pointed towards the right of the target line, while a closed face is pointed towards the left (for right-handed players- The opposite for lefties).
Most golfers consider the square face to be ideal because the other two types may cause problems, especially for beginners who do not have a lot of control over their clubface. For instance, unintentionally opening your clubface is one of the most common causes of slices (sidespin that causes the ball to curve mid-air) or push shots (the ball flying straight towards the right of the target line). Golfers who tend to slice a lot sometimes recourse to drivers that are intentionally closed to counter the issue.
Understanding factors like face angle is crucial for both left and right-handed golfers. For those looking for equipment suited to their swing mechanics, we’ve compiled a helpful guide on choosing golf simulators for left and right-handed use.
Spin Rate
Golf simulators also calculate the ball’s spin rate after impact. This refers to the ball’s amount of circular spin and is expressed using RMPs (revolutions per minute). The spin rate is responsible for how high and far the ball will travel. The higher the spin rate, the higher the ball flies and the shorter the distance, and vice versa.
Most golfers prefer to have a lower spin rate, especially in windy conditions (and even more if the player is hitting into the wind). In such situations, the wind will cause the ball to spin faster and fly much higher, ultimately ruining the total distance of the shot.
Smash Factor
The smash factor is the measurement of the amount of energy that is transferred from the clubface to the ball at impact. A higher smash factor means that more energy goes from the clubface to the ball and results in a longer distance.
The smash factor of a golf shot is calculated by dividing the ball speed by the clubhead speed. So, if you swing a driver at a 100 MPH clubhead speed and generate a ball speed of 150 MPH, then the smash factor of your shot is 1.5.
Dynamic Loft
This is the amount of vertical loft of the clubface at the moment of impact and is measured relative to the horizon. It is closely related to the ball launch angle as it affects how high and how far the ball will fly.
Golfers usually try to create a proper dynamic loft to generate an optimal carry distance. If the dynamic loft is too low, the ball will fly very low (and may end up hitting obstacles). On the other hand, if the dynamic loft is too high, the ball will fly so high that the distance is dramatically reduced (because of an ascent and descent angle which is too sharp).
Carry
Carry (or carry distance) refers to the distance that the ball travels through the air before hitting the ground for the first time, as opposed to total distance (the whole distance that the ball travels before it completely stops moving_ including the bounces).
Carry is especially important when hitting over a hazard, water, or a raised green. The player needs to make sure that the carry distance is enough for the ball to go over the obstacles or land over the raised green. It is correlated to the club’s loft, as a lower club loft angle will produce a longer carry distance, while a higher loft generates shorter carry.
How Does Putting Work on a Golf Simulator?
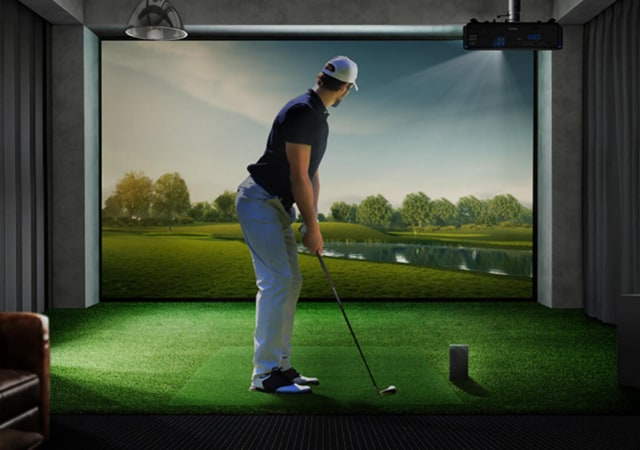

Putting is a big challenge to almost all golf simulators (and chipping too). It is not easy to put on a screen because of the lack of depth of field perception. That is, it’s not easy for a golfer to calculate the distance that the ball needs to go when the screen is only a few feet away from him/her.
To overcome this problem, most golf simulators use some sort of “virtual putting green” where the user can practice his/her putting skills. This is done by having the computer program simulate the actual putting surface as well as the hole. The player then hits the simulated ball into the virtual cup.
The virtual putting surface may be made up of several different surfaces such as grass or sand. Each one has its own characteristics. For instance, the grass has a certain height, density, and roughness. The sand has a certain hardness, weight, and color.
The following video (5 minutes 1 second) shows how putting works on a golf simulator.
In order to make the simulation more realistic, the software will also include a wind effect. If the wind is blowing towards the player, he/she will feel like the ball is being blown off course. Thus, the software will adjust the trajectory of the ball accordingly.
There are many ways to set up the virtual putting surface. Some golf simulators allow the user to choose from a variety of terrain types while others offer the option of creating custom landscapes.
Most golf simulators have a feature called “putting mode”. When you select this mode, the program will display an image of the hole along with a line showing the direction of the intended shot. You then hit the ball and watch the screen to see if your shot was successful.
Putting on a golf simulator will need an adjustment time for the player to get used to it. It will seem and feel a bit weird at first, but as you keep practicing, you will surely get hold of your putting and chipping game on your golf simulator.
Will a Golf Simulator Help Your Game?

The answer to this question is: Yes, definitely!
Having an indoor golf simulator will help you practice your favorite game any time you want, regardless of any constraints like time, weather, or distance to the nearest golf club. How can this affect your game, you may ask?
Well, it means that you will be able to practice golf more often and whenever you feel like it: early in the morning, after work, late at night, etc. More practice time means more chances to progress and improve your game.
Moreover, the readings that your golf simulator provides will be extremely useful, as you won’t be practicing blindly (not knowing what you are doing right or wrong). Instead, the simulator will give you instant feedback on your swings. Later on, you can compare all the data to track your improvement and plan objectives for your next practice session.
Some simulator manufacturers offer free instructional videos with their software bundles. You can benefit from the experience of some renowned professional players and golf instructors without the need to leave your house.
But it’s also important to remember that not all golf simulators are created equal. The technology, precision, and overall experience can vary greatly depending on the model you choose. To help you make an informed decision and ensure that you get a simulator that suits your specific needs and budget, we have compiled a guide to the best golf simulator. This comprehensive guide breaks down the features, pros, and cons of the leading simulators on the market, making it easier for you to choose the right one for your golfing needs.
Or if you wish to know more about how a golf simulator can help your game, you can always check out our detailed dedicated article in which we answer the question: Is A Golf Simulator Worth It?
Final Thoughts
Golf simulators have considerably grown in popularity over the last few years because of the numerous benefits they provide for golfers of different levels. If you are a golf enthusiast, then you should consider purchasing a golf simulation package to help you improve your golf game fast!
Having a home golf simulator allows you to play virtual golf rounds on the most prestigious, world-class golf courses worldwide (such as Pebble Beach, PGA National, Muirfield Village, etc.). It also provides a virtual practice range to work on your swings any time you wish to, as well as a plethora of other useful features.
In this article, we went through the details of golf simulator operations. We depicted all the processes, hardware, and software involved in the process of virtual golf simulation. The objective was to dissect the virtual golf experience for anyone wishing to know more about how exactly a golf simulator works.
If you still have any questions or comments about golf simulators, feel free to contact us. We will gladly provide assistance as much as we can!





